Does the Laser Welding Machine Require Shielding Gas?
![[field:title /]](https://www.acctekgroup.com/templets/youben/images/shijian.png)
![[field:title /]](https://www.acctekgroup.com/templets/youben/images/zuozhe.png)
![[field:title /]](https://www.acctekgroup.com/templets/youben/images/cishu.png)
In this article, we’ll explore the role of shielding gas in laser welding, its types, and useful tips for your welding operation to help you make an informed decision based on your welding needs.
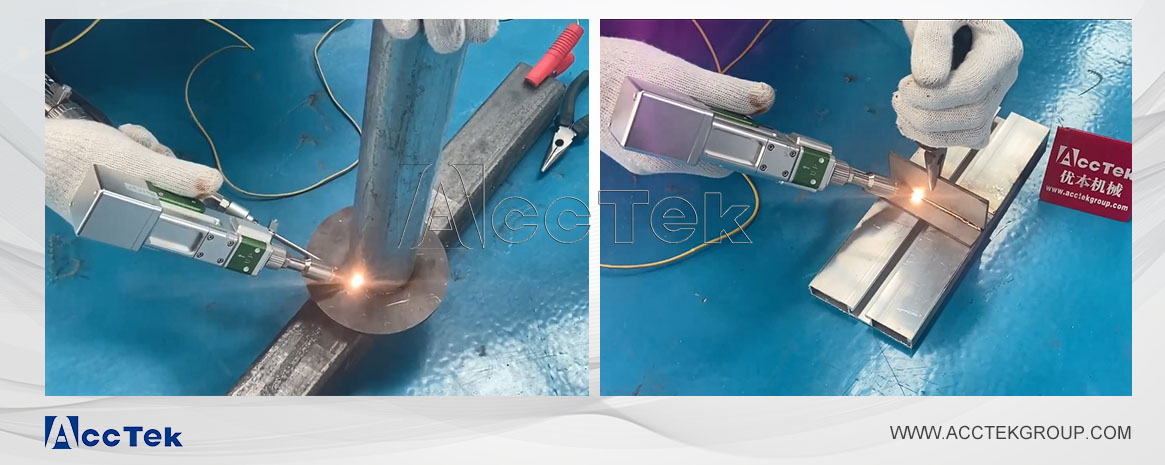
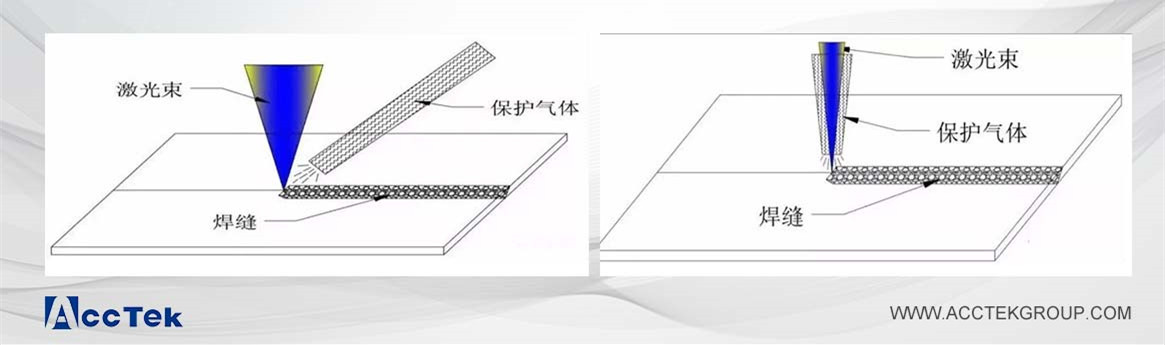
Laser welding machines have become a go-to solution for industries demanding precision, efficiency, and high-quality welding results. However, a common question arises: does a laser welding machine require shielding gas? The answer is yes, most laser welding machines require shielding gas to ensure optimal welding quality. Compressed air is the most common and basic shielding gas. Depending on the type of welding material and welding process requirements, you can also choose argon, helium, oxygen or CO2 as the shielding gas.
Shielding gas is a non-reactive or semi-reactive gas used in welding processes to protect the molten weld pool and the surrounding heated area from atmospheric contamination. It forms a protective barrier that prevents harmful interactions with oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen in the air. Shielding gases are beneficial in maintaining weld quality, ensuring durability, and achieving optimal performance in laser welding.
Role of Shielding Gas in Laser Welding
Shielding gas is indispensable in laser welding for protecting the weld pool, ensuring high-quality results, and improving the overall efficiency of the process. Here are their key roles:
Protects the Weld Pool from Oxidation: Oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere can react with the molten metal, causing defects like porosity, oxidation, and weld discoloration. Shielding gas isolates the weld pool, preventing these reactions and ensuring a clean, high-quality weld.
Enhances Weld Quality: The use of shielding gas helps produce smoother, more uniform welds with minimal defects such as cracks, inclusions, or voids. It stabilizes the laser beam's interaction with the material, leading to consistent results.
Reduces Spatter: Shielding gas minimizes spatter formation by directing excess molten metal away from the weld area, resulting in a cleaner work environment and reduced post-weld cleanup.
Supports Penetration and Efficiency: Certain shielding gases (e.g., helium) enhance heat transfer into the material, enabling deeper penetration and more efficient welding. This allows for faster welding speeds and improved productivity.
Protects Laser Optics: Shielding gas can shield the laser's optics from contaminants like smoke, fumes, and metal debris, maintaining the precision and longevity of the equipment.
Types of Shielding Gases Used in Laser Welding
In laser welding, different gases offer unique properties, making them suitable for specific materials and applications. Here are the main types of shielding gases commonly used in laser welding:
Compressed Air: Compressed air, a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace gases, is sometimes used as a shielding gas in laser welding for non-critical applications or materials. It serves as a cost-effective alternative for protecting the weld area, assisting with spatter reduction, and cooling the weld zone. However, the presence of oxygen in compressed air can cause oxidation and discoloration, making it less suitable for reactive metal welding like aluminum. Compressed air is typically used in low-cost operations or when a pristine weld quality is not the highest priority.
Argon: Argon is a widely used inert shielding gas in laser welding due to its excellent protective properties and affordability. Its heavy density effectively blankets the weld pool, preventing contamination from atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. Argon is especially suitable for welding reactive metals such as aluminum and stainless steel, as it produces smooth, clean welds with minimal spatter. However, its low thermal conductivity can limit penetration depth in thicker materials, making it better suited for precision and aesthetic welding applications.
Helium: Helium is an inert gas with high thermal conductivity, making it ideal for deep penetration laser welding applications, particularly for thicker materials like stainless steel and copper. Its lightweight nature allows for better dispersion of heat, reducing porosity and enhancing weld quality. Helium also stabilizes the laser beam, leading to consistent results in high-power welding. However, it is more expensive than argon and requires higher flow rates due to its low density, which can increase operational costs.
Oxygen: Oxygen is a reactive shielding gas used selectively in laser welding to enhance weld penetration and improve the cutting efficiency of certain metals. It reacts with the molten material to create an exothermic reaction, which adds heat and aids in deeper penetration. Oxygen is commonly used for welding carbon steel, as it can improve the mechanical properties of the weld. However, its reactivity can lead to oxidation and discoloration, making it unsuitable for materials that require a pristine finish, such as aluminum or stainless steel.
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Carbon dioxide is a semi-reactive shielding gas often used in laser welding for cost-effective applications involving mild and carbon steel. It provides good weld penetration and arc stability but may cause oxidation, leading to rougher weld surfaces and increased spatter. While it is not suitable for reactive metals, CO₂ can be mixed with argon or other gases to improve weld quality and minimize oxidation. Its affordability makes it a practical choice for large-scale or less precision-critical welding projects.
Practical Tips for Using Shielding Gas in Laser Welding
Proper use of shielding gas in laser welding is beneficial for achieving high-quality welds and maximizing the efficiency of the process. Here are some practical tips to help you get the best results:
Choose the Right Shielding Gas: Selecting the correct shielding gas is the first step to achieving the best weld quality. Argon is ideal for reactive metals like aluminum and titanium, helium is preferred for thick materials requiring deep penetration, and nitrogen is often used for stainless steel to enhance corrosion resistance. For cost-effective options, carbon dioxide can be considered for mild steel.
Ensure Proper Gas Flow Rate: Maintaining the correct gas flow rate is beneficial to provide effective coverage and protection to the weld pool. A flow rate that is too low may result in atmospheric contamination, while excessive flow can create turbulence and introduce defects. Adjust the flow rate based on the material, thickness, and nozzle size, ensuring a stable and sufficient gas shield over the weld area.
Position the Gas Nozzle Correctly: The gas nozzle must be positioned at the right angle and distance from the weld pool to ensure even gas distribution and protection. Incorrect positioning can lead to uneven shielding, weld defects, or contamination. Using the correct nozzle size and maintaining a steady gas flow helps achieve a smooth and defect-free weld.
Minimize External Interference: Shielding gas effectiveness can be compromised by external factors like drafts, wind, or contaminants in the welding area. To maintain optimal shielding, weld in a controlled environment, free from strong air currents or dust. This ensures consistent gas coverage and prevents issues like oxidation or porosity in the weld.
Test and Calibrate Parameters: Before beginning a welding project, perform trial welds to test gas flow rates, nozzle positioning, and gas types. Fine-tune these parameters based on the material, joint design, and desired results. Testing ensures optimal shielding gas performance and minimizes welding defects during production.
Most laser welding applications require a shielding gas to achieve optimal results, and the type selected depends on the welding material and weld quality requirements. Understanding the role and proper use of shielding gas empowers welders to make informed decisions, resulting in cleaner, stronger, and more reliable welds. For precise guidance, consult your laser welding machine's manufacturer to ensure the best outcomes for your welding needs.
AccTek Laser, a professional laser welding machine manufacturer in China, excels in providing advanced laser welding solutions tailored to diverse industrial applications. With a focus on precision, efficiency, and innovation, we deliver high-quality machines designed to enhance weld quality and streamline production processes. For businesses seeking laser welding equipment backed by excellent customer support, AccTek Laser is a trusted and dependable partner.
Product Directory
Copyright © Jinan AccTek Machinery Co.,Ltd